Agents API
StackSpot AI provides an API that allows you to directly trigger an Agent and receive responses via Server-Sent Events (SSE) or REST. With this functionality, you can:
- Use the API from any system, service, or pipeline.
- Make authenticated calls using a Personal Access Token (PAT) or a Service Credential.
- Get responses from an LLM using the various enrichment features of StackSpot AI.
When to use the Agents API?
- To integrate a StackSpot AI Agent into other systems, applications, or automations.
- To trigger Agents in CI/CD flows, pipelines, or development workflows.
- To create custom integrations, you receive contextualized responses within your ecosystem.
All your Agent's settings are considered in API calls, such as LLM, Knowledge Source, etc.
How to integrate the Agents API
Prerequisites
- Understand how to use APIs effectively.
- You need a Personal Access Token (PAT) or a Service Credential from StackSpot.
- After you generate your token (PAT or Service Credential), you can reuse it whenever you need to perform integrations via API in StackSpot AI. There is no need to create a new token for each use.
In the StackSpot Portal
Step 1. Access and log in to the StackSpot AI Portal;
Step 2. In the 'Contents' section, click on 'Agents' and select your Agent. Go to the API Usage tab;
If you haven't created an Agent yet, see how to create one here.
Step 3. You will see ready-to-use code examples. Enable the parameters as needed:
- Extra Knowledge Source Selection: The Knowledge Sources you add here will be included in the similarity search performed by this Agent's API.
- Return Knowledge Sources: Includes the IDs of the Knowledge Sources used in the chat responses.
- Deep Knowledge Sources: Enables more detailed and accurate searches within the Knowledge Sources, exploring Knowledge Objects to provide more comprehensive answers.
- Streaming: When enabled, you receive responses in real-time as they are generated.
- Keep Conversation: When enabled, the Agent considers previous messages to build the response. A
conversationIDis generated so you can continue the conversation later. - Send files: Allows you to add your files to the chat, generating file IDs and inserting them into the snippet in the Portal—demonstrating how you can make requests to Agents and also use file uploads.
StackSpot AI generates scripts in shell script format by default. If you need the script in another programming language, simply ask StackSpot AI to convert it for you.
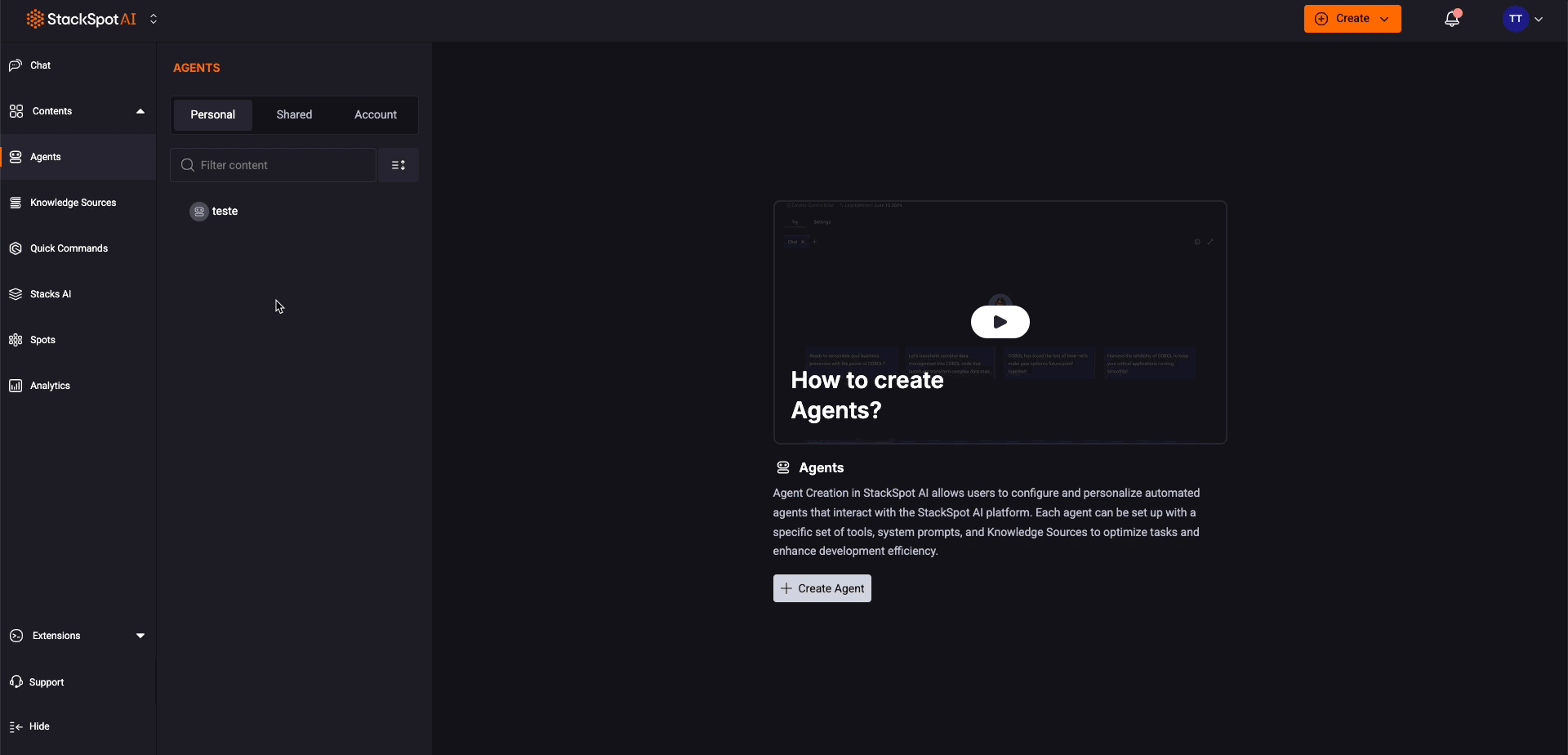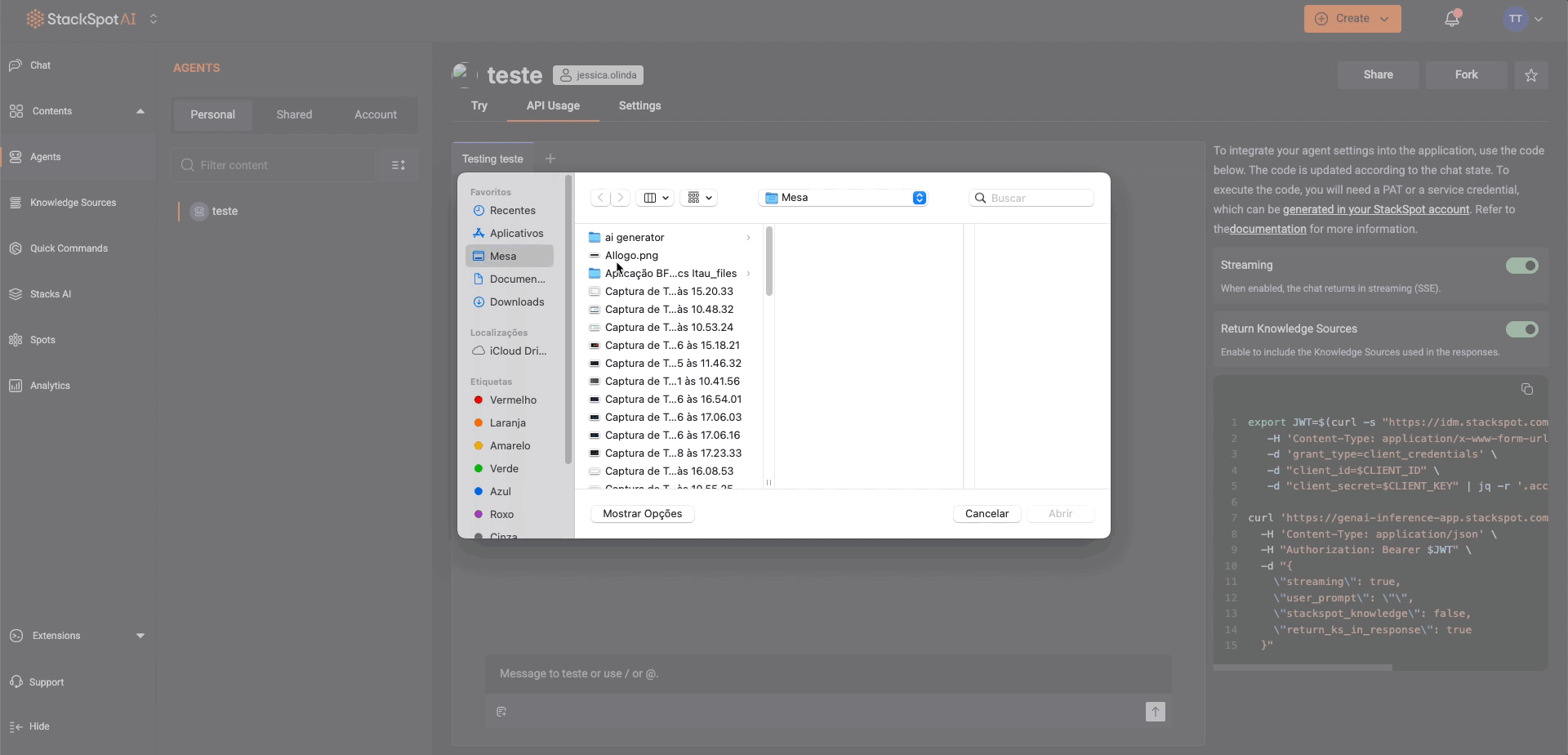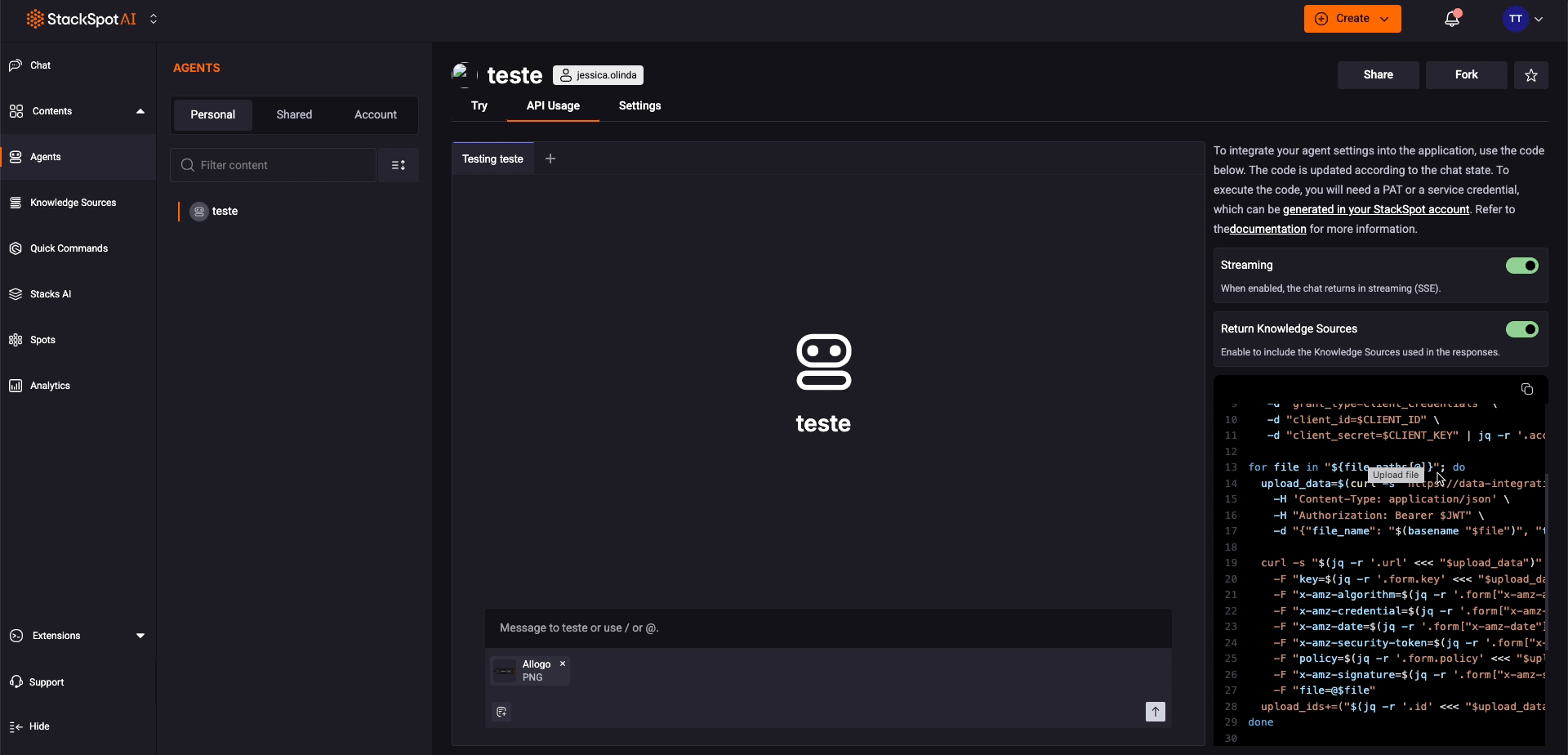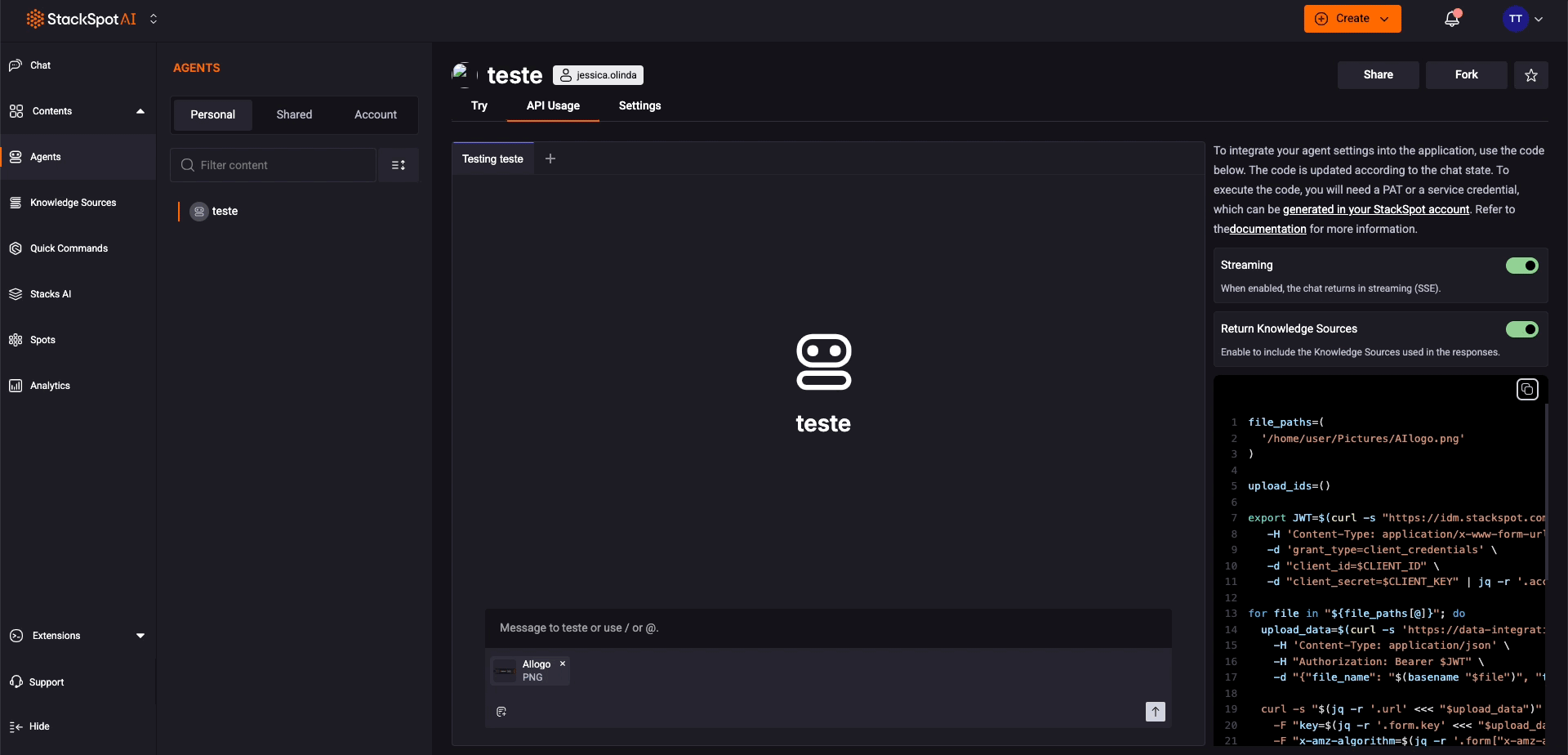
Step 4. Copy the generated code and use it in your application to complete the integration.
API Example
- Request Example:
curl -X POST "{{agent-app-url}}/v1/agent/{{agentId}}/chat" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"streaming": true,
"user_prompt": "What is an API?",
"stackspot_knowledge": "true",
"return_ks_in_response": false
}'
- Response Example:
{
"message": "An API (short for Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and definitions that allow different systems, applications, or software components to communicate with each other.",
"stop_reason": "stop",
"tokens": {
"user": 8,
"enrichment": 3083,
"output": 413
}
}
- Response fields:
stop_reason: Indicates why the response has finished. It is relevant when streaming responses are used. Since streaming was not utilized in the previous example, this field is presented first in the response. tokens: This section outlines the token usage for the request, broken down into three parts:user: The number of tokens used to process the user's prompt.enrichment: Tokens utilized to enhance the response, such as those for searches in Knowledge Sources.output: Tokens spent on generating the final response from the Agent.
API Example with conversation_id.
*conversation_id: If the use_conversation parameter is set to true, the response will return a conversation_id. This ID preserves the conversation context for future interactions.
- Request:
curl -X POST "{{agent-app-url}}/v1/agent/{{agentId}}/chat" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"streaming": true,
"user_prompt": "What is an API?",
"stackspot_knowledge": "true",
"return_ks_in_response": false
"use_conversation": true
}'
- Response example:
{
"message": "An API (short for Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and definitions that allow different systems, applications, or software components to communicate with each other.",
"stop_reason": "stop",
"tokens": {
"user": 8,
"enrichment": 3083,
"output": 413
},
"upload_ids": {},
"knowledge_source_id": [],
"source": [],
"cross_account_source": [],
"tools_id": [],
"conversation_id": "01K9T3D5752EMVMDJTSEW536AP"
}
-
Include the
conversation_idin your next request to maintain the context. See the example below: -
Request:
curl -X POST "{{agent-app-url}}/v1/agent/{{agentId}}/chat" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"streaming": true,
"user_prompt": "And what are the types?",
"stackspot_knowledge": "true",
"return_ks_in_response": false
"use_conversation": true,
"conversation_id": "01K9T3D5752EMVMDJTSEW536AP"
}'
- Response:
{
"message": "1. Web APIs: Enable communication between servers and clients using protocols like HTTP/HTTPS, commonly used in web applications and online services. 2. Operating System APIs: Allow applications to interact with the operating system, such as Windows APIs or POSIX for Unix/Linux systems. 3. Library or Framework APIs: Provide specific functionalities of a library or framework, like jQuery APIs in JavaScript or TensorFlow APIs in Python. 4. Hardware APIs: Facilitate interaction with hardware devices, enabling applications to control peripherals like printers and cameras. 5. Database APIs: Allow applications to access and manipulate data stored in a database, such as SQL or MongoDB APIs. 6. Service APIs: Used to interact with external services, such as payment APIs (Stripe, PayPal) or social media APIs (Facebook, Twitter).",
"stop_reason": "stop",
"tokens": {
"user": 8,
"enrichment": 3083,
"output": 413
},
"upload_ids": {},
"knowledge_source_id": [],
"source": [],
"cross_account_source": [],
"tools_id": [],
"conversation_id": "01K9T3D5752EMVMDJTSEW536AP"
}
Example in Python with Flask API
The following code demonstrates two services: one for authenticating with your StackSpot account and another for sending a message to an agent associated with your account. The API will be referred to as "project-agent-api," and its structure is as follows:
Project structureproject-agent-api/
├── src/
│ ├── routes/
│ │ ├── stackspot_agent.py
│ │ └── stackspot_service.py
│ └── models/
├── .env
├── main.py
└── requirements.txt
Authentication Service
stackspot_auth.pyimport requests
url = "https://idm.stackspot.com/{{your_account_realm}}/oidc/oauth/token"
payload = 'client_id={{client_id}}&grant_type=client_credentials&client_secret={{client_secret}}'
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Key': 'Authorization',
'Value': 'Bearer your_token'
}
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
print(response.text)
Send message to an Agent
stackspot_agent.pyimport requests
import json
url = "https://genai-inference-app.stackspot.com/v1/agent/{{Agent-ID}}/chat"
payload = json.dumps({
"streaming": True,
"user-prompt": "how do I create an app using stk cli?",
"stackspot_knowledge": True,
"return_ks_in_response": False
})
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer {{your_token}}'
}
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
print(response.text)
Use environment variables for local testing and secrets in production when handling sensitive authentication data for StackSpot and Agent Authorization.