Create Quick Commands with Conditionals
You can create Quick Commands that use conditionals to control what happens next in your workflow based on specific answers or criteria. This feature helps you build more dynamic and responsive workflows, making your interactions with StackSpot AI more efficient and tailored to your needs.
You can set conditions based on answers in the workflow and choose which item will run next based on these conditions.
Learn below how to create your Quick Command with Conditionals:
Requirements
- Have a Quick Command created. You can create an IDE or Remote type.
Learn each step in the following documentation sections:
Conditionals
You can add Conditionals to the Quick Commands you are creating; the execution of the flow will depend on the conditionals. Follow the steps below:
Step 1. After starting to create your Quick Command, click the ‘Conditional‘ box;

Step 2. Click the ‘Route‘ button to add your Routes;
Step 3. Add the rules for each Route, insert the values:
- 3.1. Add the input:
input_dataor a previous step of the Quick Command you created.
Example: {{slug-step.answer}}, {{slug-step.status}} or {{slug-step.data}}
- 3.2. Choose the operator:
is equal to,is not equals to,contains,does not contain,starts with,ends with,is greater than,is less than,is greater than or equal to,is less than or equal to,is empty,is not empty,is defined,is undefined,contains any of,contains all of.
3.3. Add the other value you want. You can add plain text; however, if it is a variable using input.data or an answer from another step, use {{ }}.
Example: {{input_data}}

The result may be false, or an error may occur if the types of compared values are incompatible.
You can add multiple Routes; use
and/orto add other expressions. Each Route follows the exact order you specify.
3.4. Link the step you want the flow to go after running the conditional.
- Expression
You can create your code expressions with the desired routes:
- Clicking the Expression tab to write your rules;
- You can also request AI to generate Jinja expressions.
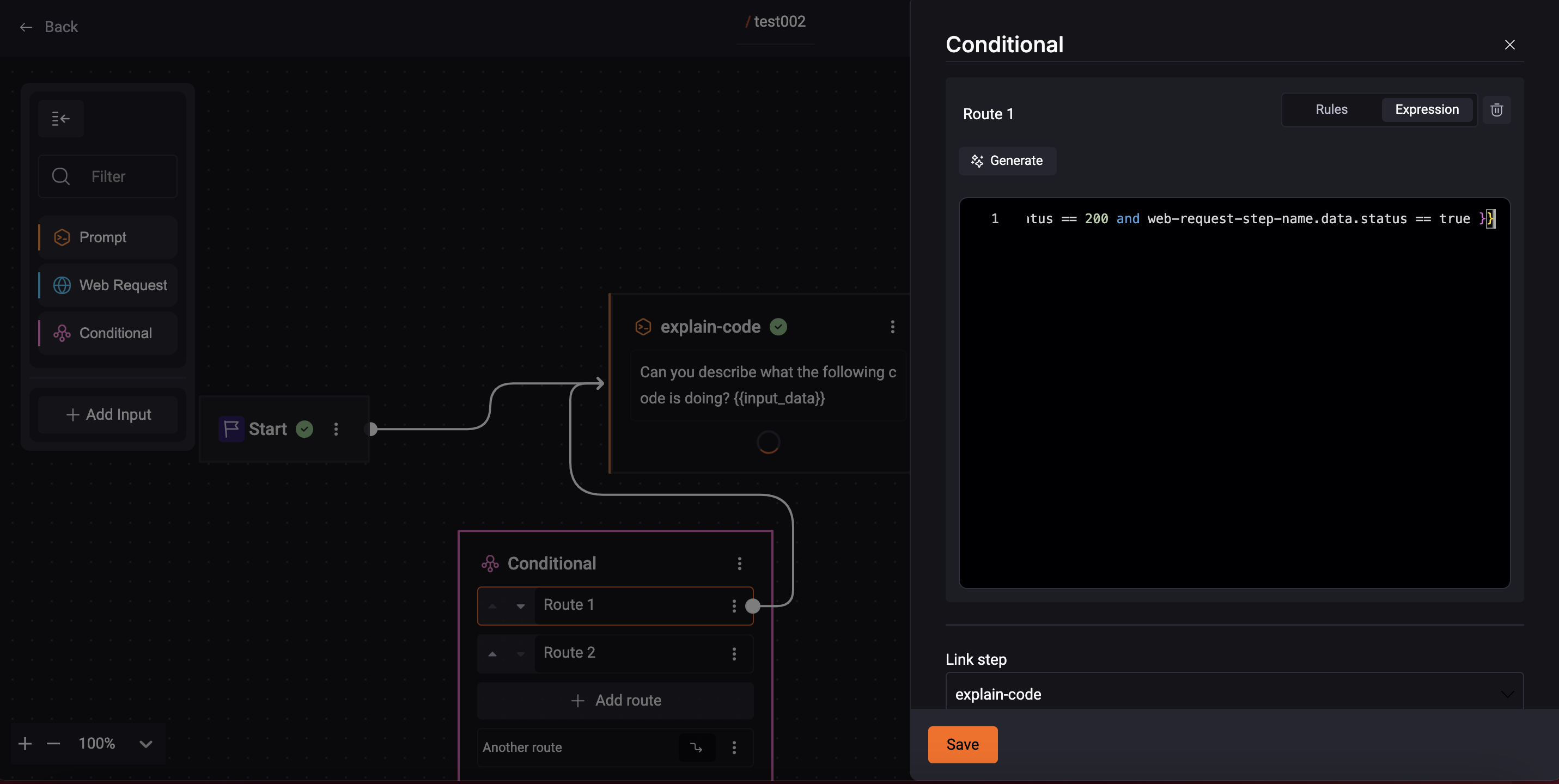
Step 4. Click the 'Save' button;
- Another Route
You need a default path. Usually, this includes an error message, which you should write down. If none of the conditions are met, the system will follow the default path.
You can also connect another route at the end of the Quick Command. If it doesn’t follow any defined route, it will end with this one.

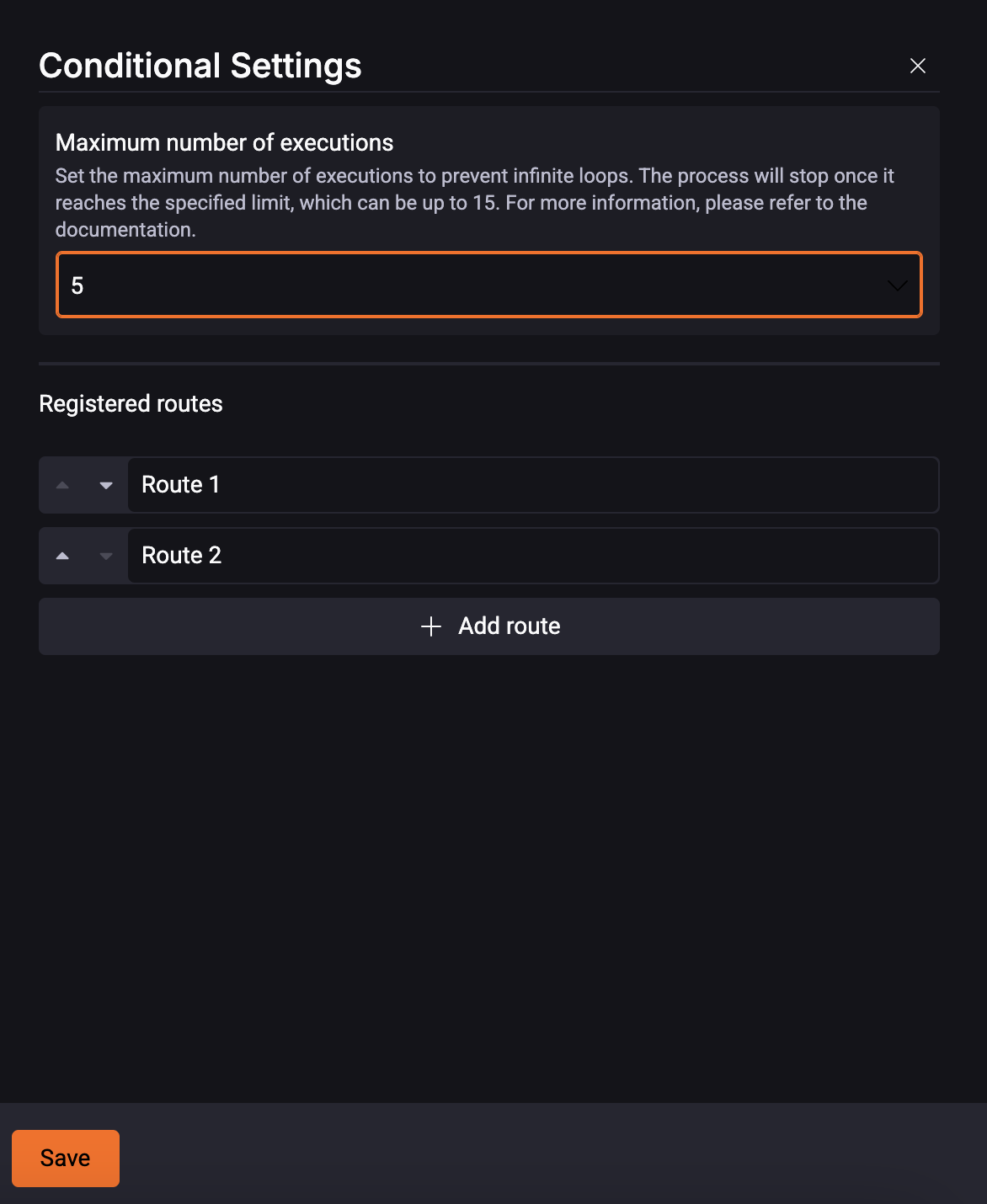
Conditional Configuration
You can specify the maximum number of times a condition will be evaluated before an error is returned.
- If the condition is true: The process advances to the next step;
- If the condition is false: It will revert to the previous step.
However, to avoid the possibility of creating a loop, you can set a limit on the number of evaluations. You can define the maximum number of executions of that condition. It indicates how many times the condition will be evaluated before returning an error.
To do that, follow the steps:
1. Click the ‘Conditional‘ box; 2. Choose a number from 1 to 15.
For each conditional, a specific path can be followed. StackSpot AI evaluates the conditionals in the order they are defined in the Remote Quick Command.
Conditional Examples
Finish Step of Quick Command with multiple routes
Imagine a Quick Command with multiple routes:
- Route 1: Calls an LLM prompt to create an endpoint (
newendpoint). - Route 2: Calls an LLM prompt to create a feature (
newfeature). - Route 3: Makes a web request to validate something external (
check_dod).
In the final step (Finish), we want to show the correct result, regardless of the route taken, without causing an error if any step was not executed.
Jinja Example in Final Result field:
{# Displays the result of the endpoint, if it exists and has a response #}
{% if newendpoint is defined and newendpoint.answer is not none and newendpoint.answer | length > 0 %}
Endpoint created: {{ newendpoint.answer }}
{# Otherwise, displays the result of the feature, if it exists and has a response #}
{% elif newfeature is defined and newfeature.answer is not none and newfeature.answer | length > 0 %}
Feature created: {{ newfeature.answer }}
{# Otherwise, displays the status and part of the web request body, if it exists #}
{% elif check_dod is defined and check_dod.status == 200 %}
External validation OK! Content: {{ check_dod.data | default('No content') }}
{# If nothing was executed, shows a default message and user data #}
{% else %}
No action performed.
User: {{ stk_ai.user_name }} ({{ stk_ai.user_mail }})
{% endif %}
is defined: Ensures the variable exists before accessing any field.default filter: Prevents errors if the field does not exist or is empty.- Access to global variables: Shows how to use user information in the fallback.
- Access to Web Request fields: Shows how to access status, headers, and body.
-
To access a JSON field returned by a Web Request:
{{ check_dod.json.nome_do_campo | default('Not informed') }} -
To show the type of content returned:
{{ check_dod.headers['Content-Type'] | default('Unknown') }}